2.0 Laptop and Portable Devices
2.1 Identify the fundamental principles of using laptops and portable devices
A laptop computer is primarily intended to be portable. The characteristics of a portable device are given below:
Functionally, there is no difference between a laptop and a desktop computer. Both run same operating systems, and applications.
We now discuss the said characteristics of laptops in more detail:
1.Laptop memory:
Laptops widely use SO-DIMM (Small Outline Dual In-line Memory Module), a smaller version of regular DIMM components used in desktops. The figure below provides a comparison of SO-DIMM and a regular DIMM package:
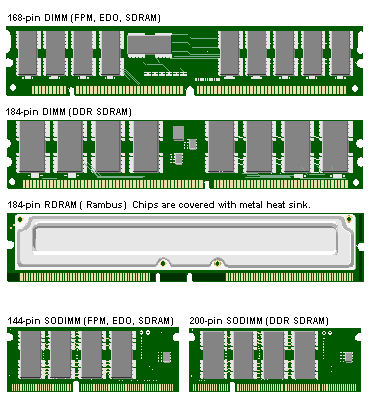
|

Above: A regular 144-pin SO-DIMM 
Above: a 200-pin DDR SO-DIMM 
Above, 240-pin DDR2 SO-DIMM |
As can be seen from the above figure, a SODIMM is roughly half the size of a regular DIMM used in desktop computers.
SDRAM (Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory) has a synchronous interface. It waits for a clock pulse before transferring data and is therefore synchronous with the computer system bus and processor. This greatly improved performance over asynchronous DRAM. Notebook SDRAM modules are usually 144-pin SO-DIMMs, as shown in fingure above.
DDR SDRAM (DDR stands for Double Data Rate) sends and receives data twice as often as SDRAM. This is achieved by transferring data on both the rising edge and the falling edge of a clock cycle. DDR memory usually comes in the form of a 200-pin DDR SO-DIMM (see image above).
Second generation DDR memory provides greater bandwidth and works on a voltage of 1.8V instead of the 2.5V used by DDR memory modules, DDR2 consumes less power than its predecessor, helping to extend notebook battery life. DDR2 memory modules are 240-pin DDR2 SO-DIMMs.
Memory Speed: Two factors are used for this measurement. 1. The operating frequency and 2. the bandwidth. SDRAM rated PC100 and PC133 work at 100MHz and 133MHz and provide 800MB/s and 1066MB/s bandwidth respectively. SDRAM and DDR/DDR2 SDRAM all use 8-byte (64bit) wide DIMM (transfer 8-byte data per clock cycle).
DDR and DDR2 memory uses different notation. DDR266 memory works at 266MHz, providing 2100MB/s bandwidth (Corresponding to the PC2100 designation). DDR400 memory is called PC3200 for its 3200MB/s bandwidth. The DDR2 533 is also called PC2 4200 or PC2 4300 but 'PC2' is used here to refer to DDR2 instead. DDR2 800 is the same as PC2 6400.
The bandwidth above is for single channel use. When memory is used in dual channel mode, the bandwidth doubles - for instance, dual channel DDR400 provides 6400MB/s (or 6.4GB/s) bandwidth as opposed to 3200MB/s for single channel DDR400.
Recommended Laptop Memory Size:
Mainstream Users: 512MB or more
A capacity of 512MB is the minimum required to run multiple simultaneous current-day programs. A capacity of 256MB can sufficient for everyday applications such as Web surfing, chatting, and office work.
Business Users: 1GB or more
If you often open and work on many large documents simultaneously, a memory of 1GB is recommended for faster switching between applications as most application data is stored in RAM instead of being accessed from the hard drive every time it is needed (relatively slow).
Multimedia Users/Gamers: 1GB or more
A memory of 1GB is the recommended minimum if you play any latest games. For multimedia processing tasks, which are similarly resource intensive, a memory of 1GB is recommended.
Mobile Workstation Users: 2GB
Professional developers require as much memory as possible. Typical applications involve image processing, video/audio editing, etc. A memory of at least 2GB memory is recommended for smooth performance.
2. Laptop Hard disks:
Laptop hard disks primarily differ from that of desktop hard disks in size and reliability. Given below are the important characteristics of laptop hard disks:
Quite unlike desktop computers, notebook computers are often moved from one place to another. To this end, enhanced vibration and shock protection are important for laptop hard drives. A typical notebook computer hard drive can take more than double the shock/vibration to that of a desktop hard drive.
Important specifications are given below:
Disclaimer: Simulationexams.com is not affiliated with any certification vendor, and Sim-Ex™ Practice Exams are written independently by SimulationExams.com and not affiliated or authorized by respective certification providers. Sim-Ex™ is a trade mark of SimulationExams.com or entity representing Simulationexams.com.A+™ is a trademark of CompTIA® organization.